Disclosure: This article was created with the assistance of AI technology and is not sponsored.
AI in Higher Education
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into various sectors has sparked a technological revolution, and higher education is no exception. With nearly half of college students already utilising AI tools, it is evident that AI is rapidly becoming an integral part of the academic landscape. This article offers a comprehensive exploration of the opportunities and challenges presented by AI integration in higher education, addressing its diverse applications, potential benefits, and ethical considerations.
Understanding the Landscape: AI Subfields and Applications
AI encompasses a range of technologies that enable machines to perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence. Several AI subfields are particularly relevant to higher education, each with distinct applications:
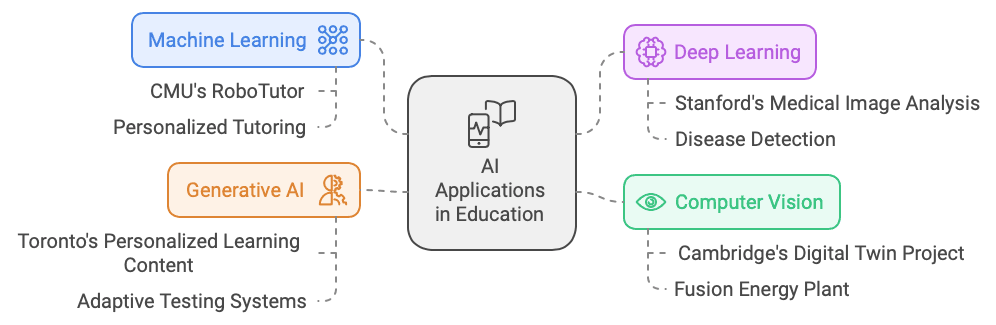
- Machine Learning (ML): ML enables AI systems to learn from data without explicit programming. Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) is a leader in ML applications in education. Their “RoboTutor” project uses ML algorithms to analyze student performance and provide personalized tutoring in reading, writing, and math.
- Deep Learning: This advanced form of ML teaches computers to process data in a manner inspired by the human brain. Stanford University’s AI Lab has been working on deep learning projects in various fields. For instance, they’ve developed deep learning models for medical image analysis, which can help detect diseases from X-rays and MRIs more accurately than human radiologists in some cases
- Computer Vision: This subfield trains computers to interpret visual data from cameras and videos. In higher education, computer vision applications include enhancing campus security, enabling automated proctoring for online exams, and supporting research in various fields. The University of Cambridge is utilizing computer vision in collaboration with the UK Atomic Energy Authority. They’re using AI and computer vision techniques to create a “digital twin” of a fusion energy plant, which will help in designing and optimizing future sustainable energy solutions
- Generative AI: Generative AI creates new content, such as text, images, audio, or video, based on the input it receives. This technology has significant potential in education for tasks such as generating personalised learning materials, creating assessment questions, and facilitating creative writing exercises. The University of Toronto, through its Vector Institute for Artificial Intelligence are working on projects that use generative AI for creating personalized learning content and adaptive testing systems
These AI subfields are being applied across various aspects of higher education:
- Teaching and Learning: Adaptive learning platforms are utilising AI to personalize the learning experience for each student. AI-powered tutoring systems offer 24/7 support and targeted practice opportunities, while automated grading systems provide efficient feedback and free up educators’ time. Real-world examples demonstrate the successful implementation of AI in diverse disciplines. The University of South Australia has implemented AI-powered games for classroom learning.
- Research: AI is accelerating research by facilitating data analysis, predictive modelling, and literature review. Researchers are using AI to gain insights from large datasets, develop new models, and accelerate scientific discoveries.
- Administration: AI is streamlining administrative tasks such as scheduling appointments, sending reminders, and managing resources. This allows staff to focus on more strategic initiatives and improve overall institutional efficiency.
The Promise of AI: Enhancing Student Success and Institutional Effectiveness
AI offers significant potential to enhance student success and improve institutional effectiveness in higher education.
For students, AI can:
- Personalise Learning: Adaptive learning platforms and AI-powered tutoring systems tailor the learning experience to individual student needs, promoting deeper understanding and engagement.
- Provide 24/7 Support: AI-powered tools offer readily available assistance and resources, addressing student questions and offering targeted practice opportunities outside of regular classroom hours.
- Enable Early Intervention: AI-powered early alert systems analyse student data to predict potential academic struggles, allowing for proactive intervention and support. Institutions utilising these systems have seen dropout rates decrease by up to 10%.
For educators, AI can:
- Automate Time-Consuming Tasks: AI can grade assignments, create quizzes, and handle administrative tasks, freeing up valuable time for educators to focus on student interaction, personalized feedback, and curriculum development.
- Provide Data-Driven Insights: AI analysis of student performance data helps educators identify areas where students are struggling, allowing for targeted adjustments to teaching strategies and more effective support.
AI also benefits institutions by:
- Improving Student Retention and Graduation Rates: Personalized learning, early intervention strategies, and readily available AI-powered support contribute to a more supportive learning environment, ultimately leading to higher student success. One university documented a 4.8% increase in graduation rates within three years of implementing their AI system.
- Enhancing Resource Allocation: AI analysis of student data can help institutions identify areas where resources are most needed, leading to more efficient and effective allocation of funding and support services.
Navigating the Challenges: Ethical Considerations and Potential Risks
While AI offers significant promise for higher education, it is crucial to acknowledge and address the ethical concerns and potential risks associated with its integration.
One significant concern is the potential for unauthorized AI use by students. Students might be tempted to utilise AI tools to complete assignments without genuinely understanding the material, undermining academic integrity and hindering the development of essential skills. Institutions must implement strategies to mitigate this risk, including:
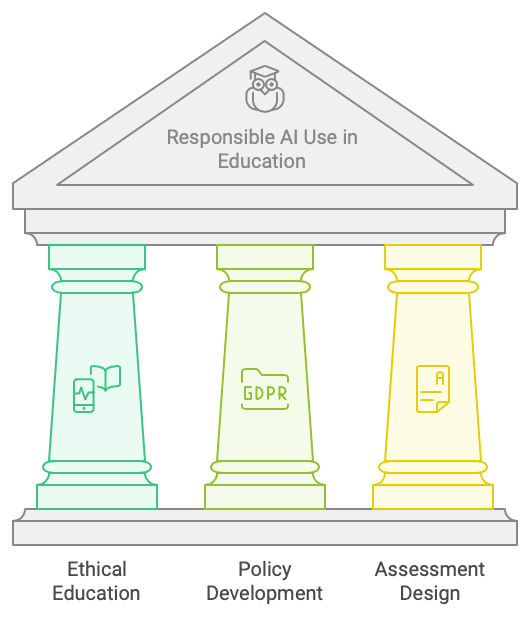
- Educating students about responsible AI use: Institutions should clearly communicate the ethical implications of AI use in academic settings, emphasizing the importance of academic integrity and the consequences of misuse.
- Developing clear policies and guidelines for AI usage: Universities should establish clear guidelines that define acceptable and unacceptable uses of AI tools in coursework and assessments.
- Designing assessments that minimise the potential for AI-generated submissions: Educators can create assignments that require higher-order thinking skills, critical analysis, and personal reflection, making it more challenging for students to rely solely on AI-generated content.
Another crucial consideration is the potential for bias in AI algorithms. AI systems are trained on data, and if that data reflects existing societal biases, the AI system can perpetuate those biases, leading to unfair assessments or unequal access to opportunities for certain student groups. To mitigate this risk, institutions must prioritize inclusive AI development and implementation, ensuring that AI systems are trained on diverse datasets and that algorithms are regularly audited for bias.
Data privacy and security are also critical concerns. The use of student data for AI applications requires careful consideration of privacy protocols and transparent communication with stakeholders. Institutions must ensure compliance with relevant data protection regulations and implement robust security measures to protect sensitive student information.
The Future of AI in Higher Education: A Call to Action
AI presents a transformative opportunity for higher education, offering the potential to enhance student success, improve institutional effectiveness, and drive innovation in teaching and learning. However, responsible and ethical implementation is paramount. Institutions must adopt a proactive approach to address the challenges and mitigate the risks associated with AI integration.
This involves:
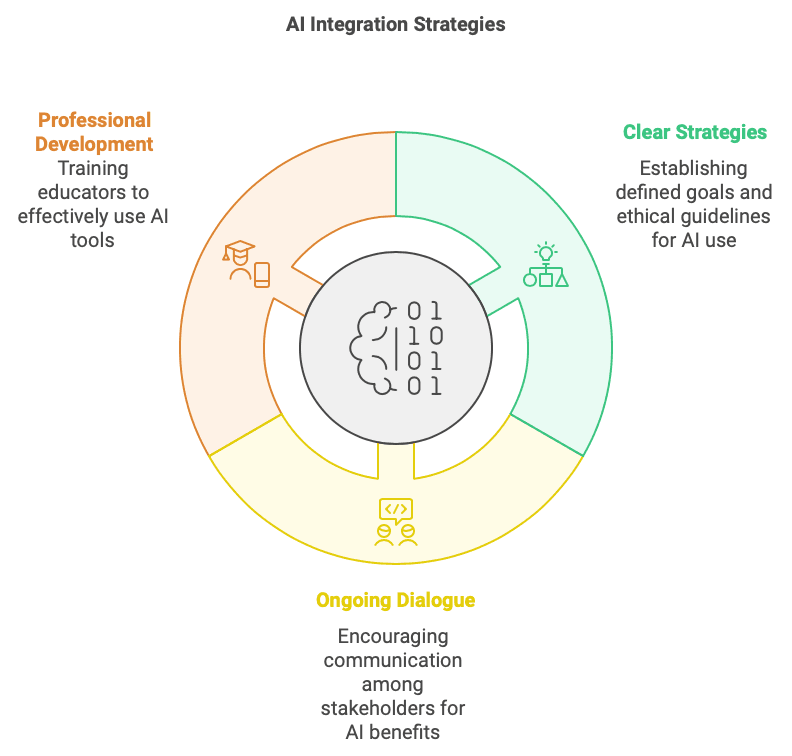
- Developing clear strategies for AI implementation: Institutions should establish clear goals and objectives for AI integration, outlining specific applications and addressing potential ethical concerns.
- Fostering ongoing dialogue and collaboration: Open communication and collaboration between students, educators, administrators, and policymakers are crucial to ensure that AI is developed and implemented in a way that benefits all stakeholders.
- Investing in professional development for faculty and staff: Equipping educators with the knowledge and skills to effectively utilise AI tools and address ethical considerations is essential for successful AI integration.
By embracing a human-centered approach to AI development and implementation, higher education institutions can leverage the transformative power of AI to create a more equitable, effective, and engaging learning environment for all.
For a deeper exploration into how AI is transforming classroom experiences, check out our blog on AI in Education: Transforming the Classroom Experience
Additional Resources:
- Learn more about AI for Lifelong Learning and how to Stay Ahead in the Age of AI.
- Explore how AI in higher education is shaping the future of universities and colleges.


